In health systems, hospitals and clinics around the world, new technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) are enabling healthcare teams to streamline workflows, read images faster and expand access to more personalized care for patients. Such tools could also help address a growing challenge in healthcare: clinician burnout.
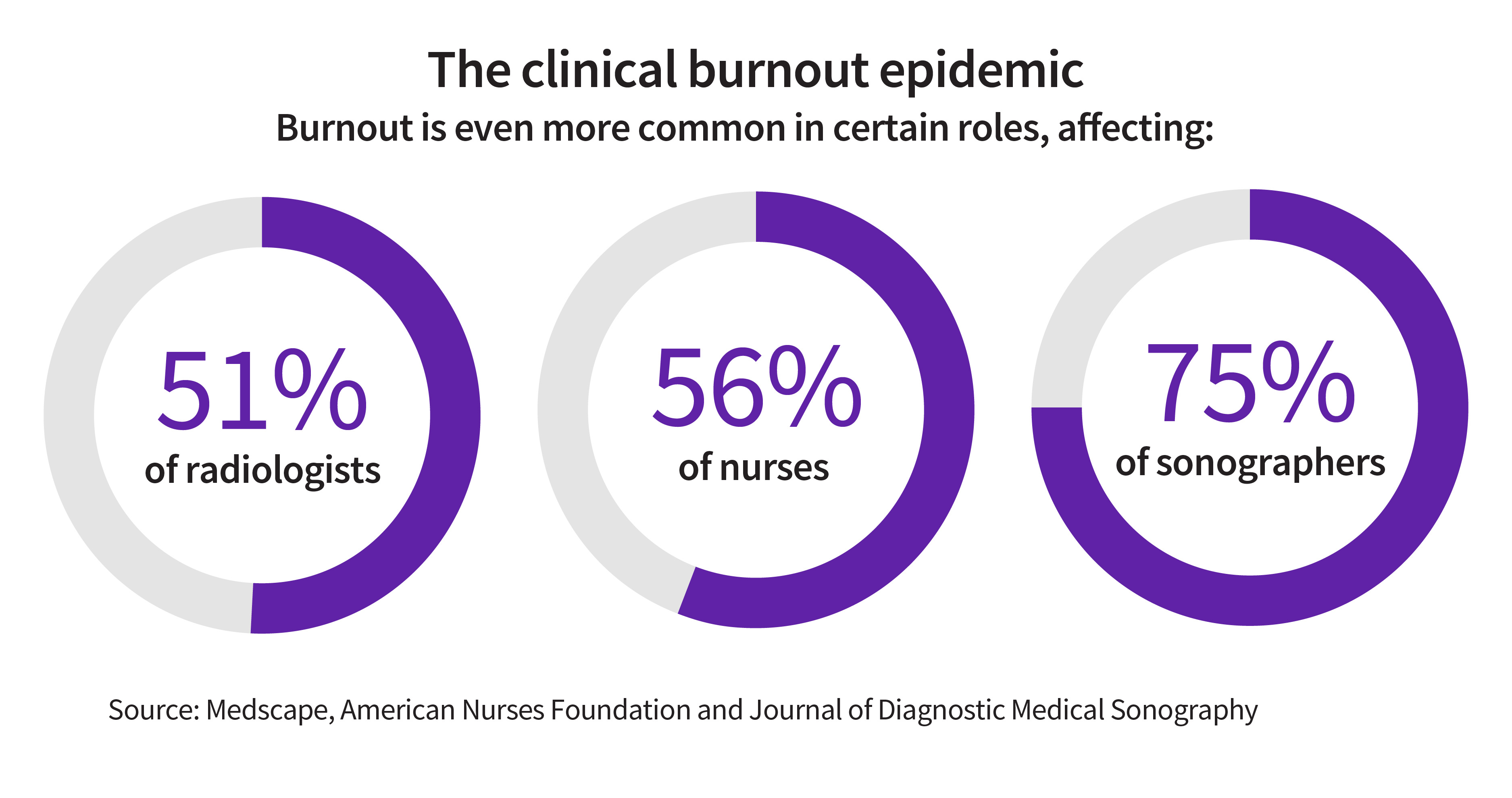
At least a quarter of healthcare workers report symptoms of burnout, such as exhaustion and a reduced sense of accomplishment. Burnout is even more common in certain roles, affecting 51% of radiologists, 56% of nurses and 75% of sonographers. Amid mounting pressures, 42% of clinicians are actively considering leaving the healthcare industry, exacerbating already critical shortages in radiology, sonography and nursing, especially in rural and remote areas.
Although it has many causes, a top contributor to clinical burnout is time pressure, particularly in patient visits and documentation. This brings a heavy administrative burden, with clinicians spending up to 28 hours per week on administrative duties alone. The healthcare worker shortage is intensifying the strain on staff as they handle more patients and work longer hours to cover gaps in personnel.
Fortunately, AI can offer solutions that could help address these challenges. By enhancing clinical decision-making, streamlining workflows and automating repetitive and time-consuming administrative tasks, AI tools could alleviate mental fatigue and burnout and allow healthcare professionals to focus on caring for patients.
Strengthening clinical decision-making and easing burnout with AI
AI-enabled tools can reduce cognitive overload by delivering insights that help healthcare professionals make more informed and timely decisions. For example, AI capabilities embedded in a PET/CT system are able to enhance image quality, which can help radiologists assess a patient’s scan. A radiologist who can help detect the spread of cancer to small lymph nodes with confidence can make a big difference in a patient’s treatment, potentially improving their outcome.
Radiologists report that excessive tasks are a top cause of burnout; AI tools can also help them interpret scans faster, reducing the read time of breast ultrasounds in one study by as much as 33% with no loss of accuracy. In addition, some research is showing that biopsy-guided ultrasound and MRI may be able to make it easier to distinguish between aggressive and slow-growing tumors to guide more targeted treatment plans.
“AI-powered MRI technology, for example, has emerged as a lifeline to a growing number of short-staffed radiology departments, enabling the clinical staff to diagnose medical problems more quickly and with greater confidence,” says Roland Rott, president and CEO of Imaging at GE HealthCare.
Using AI to optimize healthcare workflows
AI can also play a key role in streamlining a hospital’s or health system’s operations. Dr. Taha Kass-Hout, global chief science and technology officer at GE HealthCare, explains that AI can detect patterns in data to help hospitals anticipate patient flow and resource needs. By analyzing historical and real-time data, predictive models can forecast bed occupancy, discharges and staff demands, enabling proactive decision-making.
Additionally, more than half of clinicians state that some patient care responsibilities could be reallocated to relieve the burden on specialists. For example, handheld ultrasound technology can help nurses perform basic cardiac assessments using AI-enabled tools. Widespread adoption of such solutions could let specialists focus on more complex cases, and could even improve access to care at facilities with limited resources for specialty imaging or specialist clinicians.
Whether a clinical specialist or a nurse, “technology and artificial intelligence are enabling healthcare professionals to spend more of their time engaging with patients,” says Elie Chaillot, president and CEO of GE HealthCare International. “AI algorithms can help clinicians identify disease more efficiently, and with accuracy, expanding access to timely diagnosis and care by enabling critical cases to be prioritized and treatment mapped out quickly. Ultimately, this will help reduce the cost of healthcare and increase access to care.”
AI-enhanced ultrasound systems can also help sonographers work more efficiently and deliver more consistent, high-quality images. Digital ultrasound platforms can automate many steps in the scanning process, enabling faster exams and lowering the chance of errors. In addition, integrated telemedicine technology allows less experienced sonographers to consult in real time with off-site experts. This level of coaching and support can boost sonographers’ confidence and minimize patient callbacks. “AI is revolutionizing medical imaging,” Rott says. “What started with image quality enhancement and scan time reduction has resulted in physicians enabling more precise diagnoses while increasing efficiency.”
Reducing the clinical administrative burden with technology
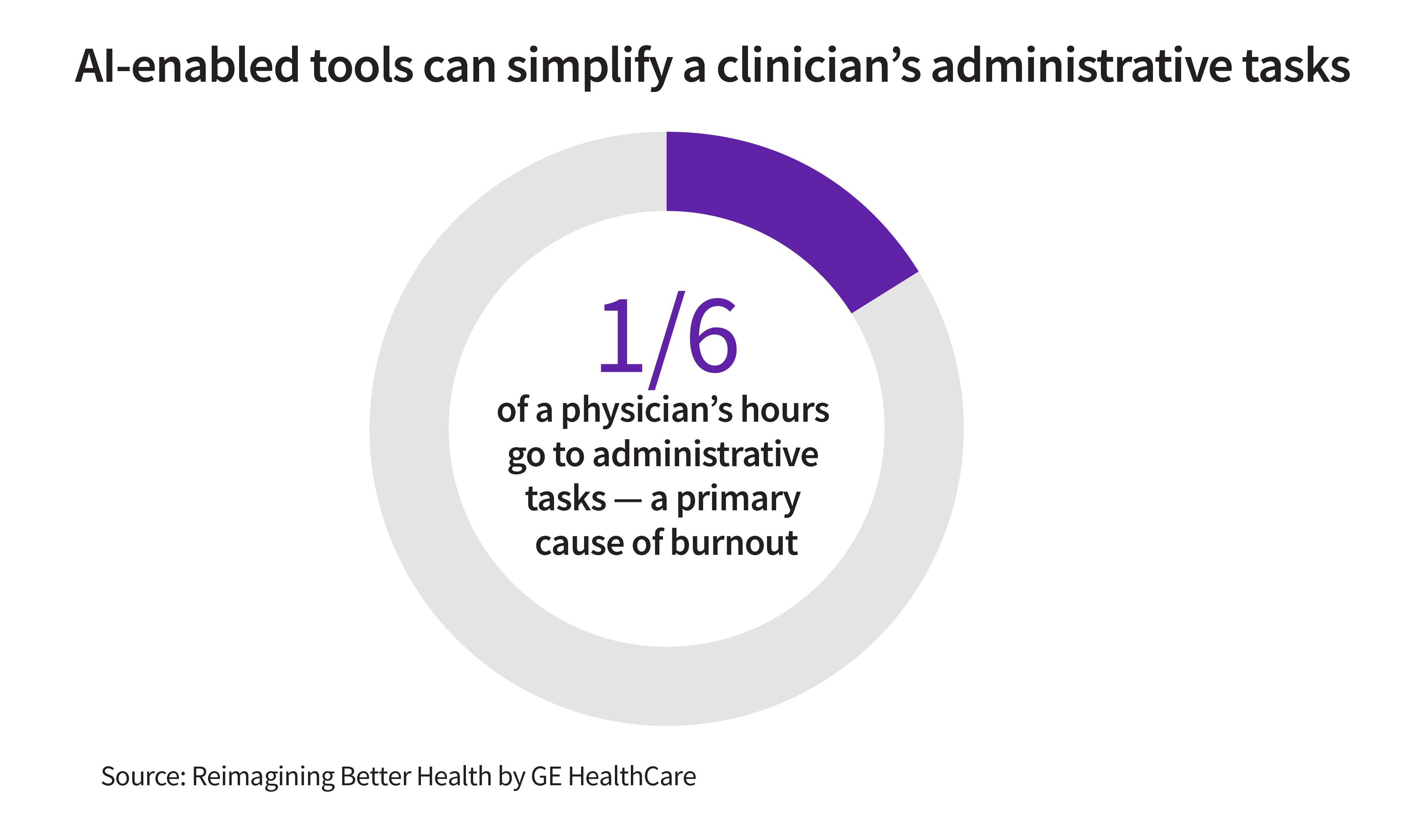
Nearly two-thirds of physicians in the U.S. cite administrative responsibilities, such as charting and paperwork, as the primary causes of burnout. AI-enabled tools can simplify these tasks, which consume one-sixth of physicians’ hours on the job. For example, AI systems can extract, format and organize patient chart information to save clinicians time—and boost their accuracy—as they write reports.
AI technologies can also lighten nurses’ administrative workload. With 18% of nurses globally reporting signs of burnout, access to tools like cloud-based virtual assistants, could make a meaningful difference. By automating routine tasks, these solutions could enable them to better focus on patient care.
Sonographers spend up to five hours per day on non-scanning activities, including exam documentation. Image management systems eliminate paper worksheets and help reduce manual data entry, helping sonographers generate accurate, customizable reports in less than a fifth of the usual time. In a department with five full-time employees performing 10 exams a day, these tools could free up 20 hours per week.
AI solutions to help solve healthcare workforce challenges
While AI is not the sole solution to clinician burnout, its integration into workflows can equip providers to face growing demand, reduce stress and improve patient care.
From staffing shortages to operational efficiencies, “AI can provide transformative solutions to some of healthcare’s most pressing challenges,” Dr. Kass-Hout says. “By using AI to optimize resource allocation, streamline the process of extracting key data from clinical documents and enhance feedback loops, hospitals can support their goal of improving patient outcomes, reducing costs and building a more resilient healthcare system.”